Site-to-Site VPN Defined
A site-to-site virtual private network (VPN) connects multiple networks together. This is often used by companies with multiple offices or branch locations. It ensures that data shared between these sites is private and secure.
Site-to-site VPNs are ideal for businesses that need to protect their data, especially if they have offices in different locations. These businesses often need access to resources on a main network, such as email servers or data storage. A site-to-site VPN allows all locations to access these resources as if they were in their own office.
Site-to-site VPNs have been around since the early days of the internet. They were made possible by the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) and the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), which helped establish how data is sent across different computers.
Today, VPNs are popular for individuals who want to hide their IP addresses, access restricted content, and ensure their internet activity is secure. However, a VPN designed for a few users does not meet the needs of large organizations that need to transfer large amounts of data quickly and safely.
Understanding VPN and Its Types
There are different types of VPNs, each with its benefits. Here’s a look at some common types:
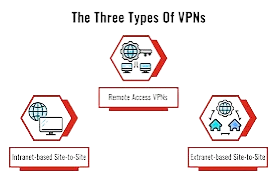
Remote Access VPNs
A remote access VPN allows users to connect to a central network from different locations. It is often used to provide employees with access to a company’s data center. This type of VPN is useful for remote workers who need access to private or sensitive information.
Remote access VPNs work like an Ethernet cable stretched over long distances, connecting employees’ devices—whether desktops, laptops, or mobile devices—to the company’s network.
Intranet-based Site-to-Site
An intranet-based site-to-site VPN connects multiple local-area networks (LANs) to create a wide-area network (WAN). This type of VPN is useful for combining resources from different offices securely, as if they were all in one location.
For example, if each office has design schematics that are frequently updated, an intranet-based site-to-site VPN allows all offices to securely access these resources, no matter where they are located.
Extranet-based Site-to-Site
Extranet-based site-to-site VPNs are used by different companies that want to share certain resources but keep others private. Each company connects to the VPN and decides what to share with others, allowing collaboration without exposing sensitive data.
How to Create a Site-to-Site VPN
Creating a site-to-site VPN involves setting up secure data transfer between locations. This can be done using an internet-based or MPLS site-to-site VPN.
Creating an Internet-based Site-to-Site VPN
An internet-based site-to-site VPN uses the internet to connect networks. You need a VPN gateway at each site to secure the data being sent.
To set this up, you create a tunnel between two networks. This tunnel is secured with gateways at each end. When data enters the tunnel, it is encrypted to protect it from unauthorized access. When the data arrives at its destination, it is decrypted by the gateway on the other end.
Creating an MPLS Site-to-Site VPN
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) is used for sending data between locations using labels rather than IP addresses. MPLS routes data directly from one location to another, avoiding extra routing that can occur with IP addresses.
To set up an MPLS VPN, you need a broadband IP network and MPLS-compatible switches and routers at each site. The data is encoded with MPLS labels and sent directly from one location to another.
Why Implement a Site-to-Site VPN
Consider a site-to-site VPN if your business has several locations and employees need to share resources from the main office. A site-to-site VPN ensures secure access to shared resources.
For example, if your company has offices in New York, Shanghai, France, and Switzerland, a site-to-site VPN will allow all employees to access the same email and data servers securely.
5 Key Components of a Site-to-Site VPN
- Watertight Security: The VPN must have strong security measures. Data should be protected while moving and when stored. Proper authorization and authentication are crucial.
- Ease of Operations: The VPN should be easy to use, ideally through a web browser. Access should be straightforward but secure, allowing employees to connect from different devices like laptops and smartphones.
- Simple and Secure Scalability: Adding new sites or users should be quick and inexpensive. If you need to move an office, setting up a new location should be simple.
- Business Continuity: A site-to-site VPN helps minimize downtime during disasters. Employees can work from home and still access resources at headquarters.
- Flexible Deployment: You can deploy new solutions across different locations in stages, allowing for manageable updates and training.
The Benefits of Managed VPN Services
Managing a site-to-site VPN can be challenging. Using managed VPN services can help you focus on your business while experts handle the VPN’s operation and security. Managed services offer scalable solutions, allowing you to add locations worldwide. They also handle setup, upgrades, and modifications, ensuring smooth connectivity and operation.

Hi, I’m Chibuzor Abraham from Nigeria. I love technology, especially VPNs, which protect your online privacy. I manage Ohiovpn.us, where I review VPN services for Ohio. Our reviews look at speed, security, and ease of use to help you find the best VPN. If you buy through our links, we get a small commission, which helps support our site at no extra cost to you.