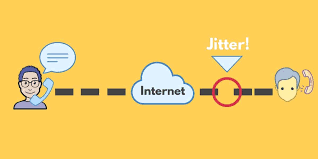
Definition of Network Jitter
Network jitter is the variation in the delay of data packets sent over a network. This means that data packets arrive at different times, which can cause problems. Jitter happens because of network congestion, packet loss, and different paths that packets take. It affects real-time applications like video calls, online games, and VoIP services.
In simple terms, jitter is the disruption in your internet connection when data packets are sent to your device. It refers to the variation in delay between when data is sent and when it is received.
How Network Jitter Works
To understand how network jitter works, you need to know a bit about how the internet functions.
Imagine you want to watch a movie online. You click “play” on your favorite website. The movie starts streaming. Since movies are large files, the internet breaks them into small data packets. These packets travel from the server to your browser when you press “play.”
Data packets have parts like the header, payload, and sometimes a trailer. These parts help servers and browsers know how to organize and reassemble the data. Think of them like Lego pieces, each with instructions on where it should go.
The journey of these packets is not always straightforward. Each packet might take a different path through various servers and is only put together correctly when it reaches your device. If your internet is fast, this happens quickly, and you don’t notice it.
But if your internet is slow or congested, packets can travel more slowly or get stuck. This causes jitter and can interrupt your movie with annoying loading screens.
Types of Network Jitter
Network jitter can happen in different ways. The most common types are:
- Constant Jitter: This type is regular and predictable. Devices can handle it better, so it’s less disruptive. While not ideal, it’s often manageable for gaming and video calls.
- Transient Jitter: This type is sudden and unpredictable. It can cause temporary problems like choppy audio or frozen video, making your browsing experience unpleasant.
- Short-term Jitter: This is brief and quick, similar to transient jitter. It might cause a small delay during a video call or a brief drop in audio quality while watching a video on social media.
Effects of Network Jitter
Network jitter can have various effects, from annoying interruptions to potential data loss. It often impacts VoIP calls, streaming services, and the quality of audio and video. High jitter can also lead to packet loss, causing errors, lost data, or the need to reload pages.
Acceptable Level of Jitter
While it’s hard to completely avoid jitter, you should try to keep it as low as possible. Ideally, jitter should be below 30 milliseconds. For a good connection, the ping should be 150 milliseconds one way and 300 milliseconds round-trip time (RTT). Lower RTT is better, ideally under 100 milliseconds, for a smooth experience.
To keep apps running well, latency should be low, and data packet loss should be no more than 1%. This helps with uninterrupted video streaming, clear audio in VoIP calls, and a lag-free browsing experience.
Causes of Network Jitter
Jitter can be caused by various factors, including:
- Slow or overcrowded wireless networks
- Poor packet prioritization
- Bad hardware performance
- Packet loss
- Network congestion
- Bandwidth issues
- Bandwidth throttling
- Firmware or software bugs
- Internet service provider (ISP) problems
Measuring Network Jitter
You can measure network jitter with different tools, depending on the type of traffic:
- Single Endpoint Jitter Testing: This measures jitter from one device to another single point in the network. You can test this by using tools designed for single endpoint measurement, pinging your IP address, or performing a traceroute.
- Double Endpoint Jitter Testing: This measures jitter on the round trip of data packets, from source to destination and back. Tools for this test support RTT and instantaneous jitter measurement.
- Bandwidth Testing: This measures how much data transfer rate is available on your network. While its main focus is on capacity, it also affects jitter. Perform this test using reliable tools several times a day to get accurate results.
How to Fix Network Jitter
Fixing network jitter can be challenging, but you can try various methods to reduce it:
- Set Up Jitter Buffering: Jitter buffering helps by temporarily storing data packets and reordering them before delivering them to the application. This can make real-time communications like VoIP and video calls smoother.
- Upgrade Ethernet Cable: Poor-quality cables can worsen network performance. Upgrade to Cat 6 or Cat 7 cables to support higher data transfer rates and reduce jitter.
- Prioritize Packets: Give priority to critical packets for real-time applications like VoIP or video streaming. This can help reduce congestion and jitter.
- Monitor Device Frequency: Devices using the same wireless frequency can cause interference. Manage your devices’ frequency bands to avoid this issue. Use a dual-band router to separate devices between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies.
- Reduce Unnecessary Bandwidth Usage: Too many devices or high-bandwidth activities at once can increase jitter. Limit streaming and other high-bandwidth activities to reduce jitter.
- Enable Quality of Service (QoS): QoS settings on many routers allow you to prioritize certain types of traffic. Give higher priority to time-sensitive data like VoIP or video streaming to reduce jitter.
- Schedule Updates: Software updates can use a lot of bandwidth. Schedule updates for late at night or during low-usage times to avoid impacting network performance.
- Choose a Good Quality VoIP Provider: The quality of your VoIP provider affects the level of jitter during calls. Select a VoIP provider known for reliability and low network latency to avoid jitter problems.

Hi, I’m Chibuzor Abraham from Nigeria. I love technology, especially VPNs, which protect your online privacy. I manage Ohiovpn.us, where I review VPN services for Ohio. Our reviews look at speed, security, and ease of use to help you find the best VPN. If you buy through our links, we get a small commission, which helps support our site at no extra cost to you.